PCB Assembly Process
PCB Assembly Process
Firstly, take you to know some brief development history of PCBA, also called PCB assembly. PCBA is the abbreviation, which means that the SMT process of the PCB finished or the process of passing through the DIP or THT. Then it is abbreviated as PCBA. In fact, it is commonly referred to as an electronic board or circuit board.
Circuit board, abbreviated as PCB, is an important electronic component and the support of electronic components. This is the earliest version. Later, the Austrians created new technologies that removed unwanted metals and added wiring, forming the version we are currently using.
Due to its position in the latter half of the electronic equipment process, PCBA is referred to as the downstream of the electronic industry. Because all electronic devices and equipment require PCBA's support, this project has the highest portion in the electronic market. There are currently huge industrial areas around the world that manufacture circuit boards (PCB).
Computers and related products, communication devices, and electronic devices are all the main consumer groups of PCBA. Including commonly computers used at home, televisions, LED lights, mobile phones, tablets, etc. Because every household is using it, PCBA's economic development is rapid and it has quickly become the top in the world.
PCBA is still developing, and to make people's lives more convenient, there are several general conditions for its development:
a. Vigorously develop HDI to make PCBs more precise and smaller.
b. PCBA also needs to ensure strong vitality and service life in order to last longer.
c. Update production equipment and manufacturing process.
In PCBA processing, SMD components and plug-in (THT, Through-hole technology) components are used.
Chapter 1: SMD components and plug-in (THT) components
So, what is the difference between SMD components and plug-in (THT) components?
1、 The difference between the two are as below:
1.1 SMD components have small size, light weight, and are easier to solder than plug-in components.
1.2 One important benefit of SMD components is that they improve the stability and reliability of the circuit; Because the SMD component has no leads, it reduces stray electric and magnetic fields, which is particularly effective in high-frequency analog circuits and high-speed digital circuits.
2、 Soldering method for both
2.1 Method for soldering SMD components:
Place the component on the solder pad, apply the prepared SMD solder paste on the surface of the component and the contact area between the solder pad, and then heat the connection between the solder pad and the SMD component with a 20W internal heating electric soldering iron (the temperature should be between 220~230 ℃). Once the solder melts, remove the electric soldering iron and wait for the solder to solidify before welding is completed. After welding, tweezers can be used to clamp the soldered components to see if there is any looseness. If there is no looseness, it means that the soldering is good. If there is looseness, reapply solder paste and weld again according to the above method.
2.2 Method for soldering THT components:
When soldering all pins, solder shall be added to the soldering iron tip, and flux shall be applied to all pins to keep them wet. Touch the end of each pin of the chip with a soldering iron tip until the solder flows into the pins. After all pins are soldered, wet the pins with flux to clean the soldering tin, so as to eliminate any short circuit and overlap. Finally, use tweezers to check whether there is faulty soldering. After the inspection, remove the flux from the circuit board and carefully wipe the hard brush along the pin direction with alcohol until the flux disappears.
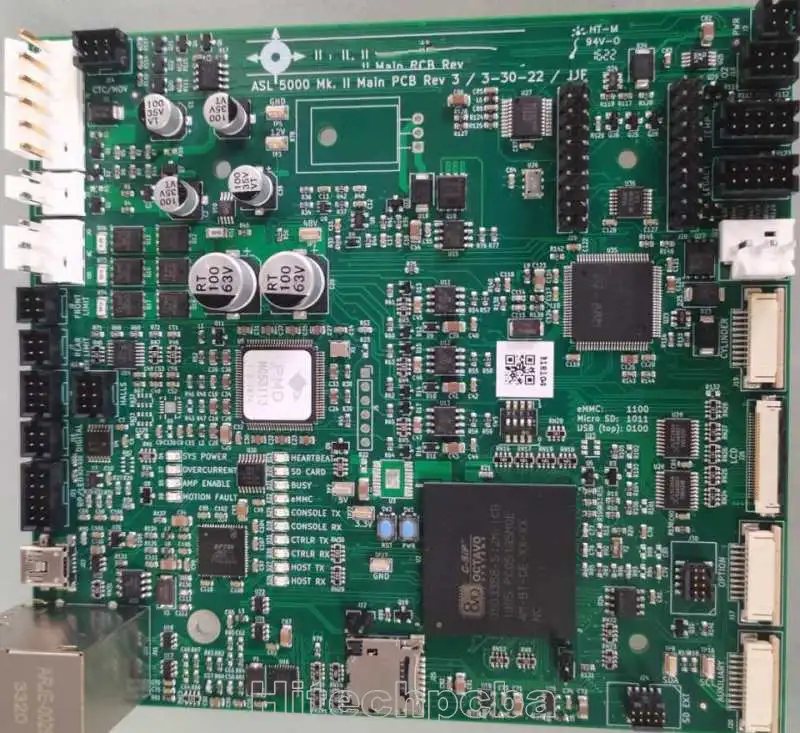
Chapter 2: Complete process of PCBA
Then, after learning something about the components, here is a complete process of PCB board assembly:
Step 1: Apply solder paste to the PCB board
In this step, obviously the stainless-steel stencil and the solder past will be used.
Solder paste should be evenly applied to the circuit board in the right PADs and locations needed.
Step 2: Use the mounting machine to Pick and place
Surface mounted components or SMDs, should be placed on a prepared PCB by an automated mounting machine. Then, the components need to be soldered onto the correct pads on the circuit boards.
Step 3: Going through the reflow to soldering the components
This process will help make the solder paste solidify and in order to adhere the components to the PCB, the solder paste needs to go into the reflow and stay for a period of time to get better soldering.
Step 4: Inspect the semi-finished PCB assembly
Once the reflow process is finished and the mount components are soldered into the correct place, comes the current PCB inspection during the SMT stage. The assembled board should be tested and inspected for functionality, such as using ICT jigs, AOI, etc.
Ways to check the PCBA quality include the basic following:
Manual inspection: A visual inspection should be made by the production worker and the person from the quality department to ensure the good quality of a PCB.
Automatic optical inspection (called AOI): An inspection method and a certain machine more appropriate for larger batches of PCBAs. An automatic optical inspection machine, or AOI machine, uses high-powered cameras, set at different angles to view the solder connections.
X-ray inspection: An inspection machine used for more complex PCBs by examining the layers of the PCB and identifying potential problems, especially for those which have BGAs, QFNs, etc.
Step 5: Insert the through-hole component
A plated through-hole, or PTH, is a hole in the PCB. It is plated through the board. Rather than soldering paste, more specialized soldering method is required for this process. Generally, after insert the components in the hole, then make the boards go into the wave soldering
Manual soldering: for the simple board, sometimes manual soldering can be used, but not recommended all the time.
Wave soldering: The automated version on manual soldering where a wave of molten solders all the holes which required the soldering at the bottom of the board at once.
Step 6: Finish the final inspection
Once all the soldering process of the PCB assembly is completed and finished, it is time to do a final inspection and functional test. This will depend on different projects’ requirements and different customers. It includes the ICT test and FCT test.
Run power and simulated signals to test the PCBs electrical characteristics. A sign that the PCB has failed is when it shows the fluctuation of electrical signals during the test.
If the PCB fails during the final inspection, it should be rechecked and retested. And the process begins all over again until a good and successful PCB is produced.
Chapter 3: Some special technology in SMT
Reflow soldering is used to melt solder paste to make electronic components soldered and fix. Reflow soldering is divided into four temperature zones, namely preheating, constant temperature, heating and cooling zones.
Each temperature zone has different functions. The ordinary reflow soldering is mainly air reflow soldering, which deals with ordinary electronic products, while products with high requirements on quality, stability and void rate (such as automotive electronics, avionics, medical electronics, etc.) will need nitrogen reflow soldering, even vacuum reflow soldering welding. That means input the nitrogen during the soldering on the reflow.
In the reflow soldering, nitrogen is usually used in heating and cooling areas. Why need to add nitrogen? Let's talk about this topic here.
There are three main reasons for adding nitrogen to reflow soldering.
1. Reduce oxidation
2. Increase wettability and improve soldering quality
3. Reduce void fraction
Here are the details as below:
1. Reduce over furnace oxidation
Because nitrogen is an inert gas, after adding nitrogen, the bottom of the reflow is occupied by nitrogen, isolating the oxygen at the bottom of the reflow, thereby reducing the contact with oxygen and reducing the oxidation reaction of PCBA through the reflow.
2. Increase wettability and improve soldering quality
Nitrogen gas occupies the bottom of the heating temperature zone, which increases the wettability of the solder paste during hot melting at high temperatures. This allows various components to be soldered better and ensures the improvement of soldering quality.
3. Reduce void fraction
Void rate has always been a technical indicator of reflow soldering. The main reason for using nitrogen to reduce the void rate is that nitrogen is an inert gas, which makes PCB pads and components largely isolate oxygen and water vapor molecules in the air, and accelerates the discharge of water molecules in the hot melt of solder paste. When cooled, the hot melt solder paste becomes solid, and there are few cavities.
Of course, adding nitrogen to reflow soldering also has the disadvantages, such as not cost-efficient, increase the probability of tombstones, enhanced wick effect, etc.
In general, whether choosing adding nitrogen depends on the certain situation and projects.
PCB Assembly Testing and Inspection
PCBA testing refers to the test of electrical conductivity and input-output value based on PCBA board with electronic components.
Why need PCBA testing?
In the design of PCB, there is a numerical relationship between different test points, such as voltage and current. However, the process flow of PCBA production and processing is very complex, including many important processes such as the PCB manufacturing process, component procurement, and inspection, SMT patch assembly, dip plug-in PCBA test. In the process of production and processing, various problems may occur due to improper equipment or operation. Therefore, it is necessary to use professional test equipment or a manual multimeter to test the test points, to verify whether the actual PCBA board meets the design requirements and ensure that each product will not have quality problems.
PCBA testing is a key step to ensure the quality of production and delivery. FCT test fixture is made according to the test point program and test steps designed by customers, and then the PCBA board is placed on the FCT test rack to complete the test.
Testing is crucial to ensure high quality products are delivered to customers. Thankfully board assemblers offer multiple layers of testing and inspection to ensure high-quality, assembled circuit boards are produced and delivered to customers. Despite all efforts to prevent errors, printed circuit board assembly is a complex process and defects sometimes occur relating to a variety of issues from incorrect component loading to failures in SMT equipment. Thorough testing and inspection occur throughout the production process to ensure problems are captured early on, ensuring high quality and yield.
Brief analysis of three PCB stencil processes
1. Solder paste stencil: As the name suggests, it is used to brush solder paste. Cut holes on a steel sheet corresponding to the PCB board solder pad. Then use solder paste to transfer and print onto the PCB board through a stencil. When printing solder paste, the solder paste is applied above the stencil, while the circuit board is placed below the stencil. Then, a scraper is used to scrape the solder paste evenly on the stencil holes (when the solder paste is squeezed, it will flow down from the stencil holes and cover the circuit board). Stick the SMD components and conduct reflow soldering welding uniformly. The plug-in components are welded manually.
2. Red glue stencil: The opening is made between the two pads of the component based on the size and type of the part. By using glue dispensing (which uses compressed air to apply red glue to the substrate through a dedicated glue dispensing head), the red glue is transferred to the PCB board through stencil points. Then insert the components, wait for the components to adhere firmly to the PCB, and then insert the plug-in components for unified wave soldering.
3. Dual process stencil: When a PCB board needs to be coated with solder paste and red glue, dual process stencil needs to be used. The dual process stencil consists of two stencil, one ordinary laser stencil and one step stencil. How to determine whether solder paste uses step stencil or red glue uses step stencil? First, understand whether to brush solder paste or red glue first. If the solder paste is applied first, then the solder paste stencil is made into a regular laser stencil, and the red glue stencil is made into a step stencil. If the red glue is applied first, then the red glue stencil is made into a regular laser stencil, and the solder paste stencil is made into a step stencil.
The quality of PCB stainless-steel stencil is mainly affected by the following factors:
1. Production process
Previously, we discussed the production process of stainless-steel stencil, and it can be seen that the best process should be laser cutting of stainless-steel stencil followed by electric polishing treatment. Chemical etching and electroforming both have processes that are prone to errors such as making longevity films, exposure, and development, and electroforming is also affected by uneven substrates.
2. Materials used
Including PCB frame, wire mesh, steel sheet, adhesive, etc. The PCB mesh frame must be able to withstand certain program relays and have good levelness; It is best to use polyester mesh as it can maintain stable tension for a long time; It is best to use 304 grade steel sheets, and matte ones will be more conducive to the rolling of solder paste (adhesive) than mirror ones; The adhesive must have sufficient strength and be able to withstand certain corrosion.
3. Opening design
The quality of the opening design has the greatest impact on the quality of the PCB stainless-steel stencil. As discussed earlier, the design of openings should consider the production process, aspect ratio, area ratio, experience value, etc.
4. Production materials
The completeness of production materials can also affect the quality of PCB stainless-steel stencil. The more complete the information, the better. At the same time, when data coexist, it should be clear which one should prevail. Also, generally speaking, using data files to create stainless-steel stencil can minimize errors as much as possible.
5. Usage method
The correct printing method can maintain the quality of the stainless-steel stencil. Conversely, incorrect printing methods such as excessive pressure or uneven PCB stainless-steel stencil or PCB during printing can cause damage to the stainless-steel stencil.
6. Cleaning
Solder paste (adhesive) is relatively easy to solidify, and if not cleaned in a timely manner, it will block the opening of the stainless-steel stencil, making it difficult to print next time. Therefore, after removing the PCB stainless-steel stencil from the machine or not printing solder paste on the printing machine for 1 hour, it should be cleaned in a timely manner.
7. Storage
The stainless-steel stencil should be stored in a specific location and should not be placed randomly to avoid accidental damage to the stainless-steel stencil. At the same time, the PCB stainless-steel stencil should not be stacked together, as it is difficult to handle and may bend the mesh frame.

0086-755-29970700
sales@hitechpcb.com; sales@hitechcircuits.com
3F, B5 Dong, Zhimeihuizhi, FuYong, Bao’an Dist. Shenzhen, GuangDong, China 518103
 Chinese
Chinese English
English Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Portuguese
Portuguese





