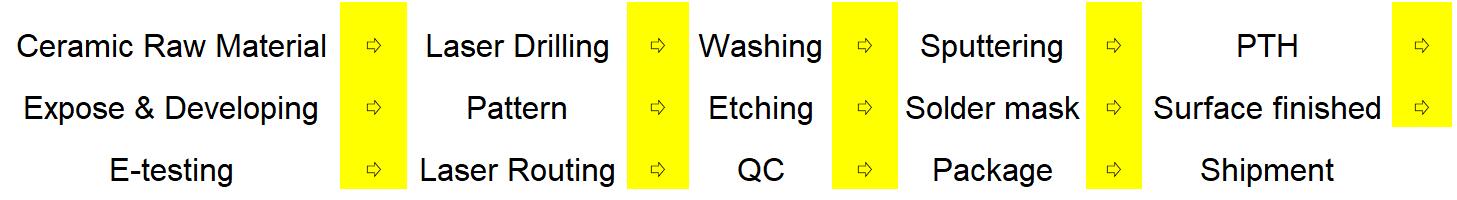
Ceramic PCB Manufacturing Process
Ceramic PCB Manufacturing Processes
Ceramic PCBs are composed of a ceramic substrate, a connection layer, and a circuit layer. Unlike Metal core PCB, ceramic PCBs do not have an insulation layer, and manufacturing the circuit layer on the ceramic substrate is difficult. How are ceramic PCBs manufactured? Let us tell you ceramic PCB manufacturing process. Ceramic printed circuit board (PCB) is an advanced material widely used in the electronics industry, combining ceramic materials’ advantages with traditional PCBs’ functions.
Ceramic PCBs have excellent thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature, high-frequency, and high-power applications. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the manufacturing process of ceramic PCBs.
Step 1: The Design
First, come up with the design for the ceramic PCB. You can achieve this using design software. Trace width calculator helps you in coming up with the details for the inner and the outer layers of the board.
Step 2: IQC for Ceramic raw material
When we received Ceramic raw material, our IQC will inspect it and write down related information.
Our Ceramic raw materials have HuaQing, ZhengTian, Maruwa, Kyocera, etc.
Step 3: Laser Drilling
Ceramic raw material is hard and can not use normal drilling bit, must be used laser drilling machine.
Before you start drilling, ensure that you place the board on a buffer material under the drill target. This will help to ensure that the enacted bore is clean.
You can now bore holes into the stack board with utmost precision. Ensure that the holes are drilled to a hairs-width.
Step 3: Washing and Sputtering
Using ultrasonic washing machine to clear the surface of Ceramic PCB, and ensure high quality.
After washing the bare board and than do sputtering process.
Step 4: Plating
When you have thoroughly cleaned the panel, you can proceed to wash it using several chemical baths.
When doing the baths, the chemical deposition process will deposit a thin layer of copper on the panel’s surface. This is usually about one micron thick.
Step 5: Expose & Developing & Pattern
In this step, you will get the lines following up the design files.
Pass the prepped panel through the yellow room. The yellow lights don’t carry UV levels that can affect photoresists.
When the panel and stencil come into contact, a generator will blast them with high UV light. This will further harden the photoresist.
You can then pass the panel through a machine that will remove the unhardened resist, which is protected by black ink opacity. In this process, you will invade the inner layers.
The sections of the panel that you have exposed from the outer layer’s photoresist stage will receive copper electroplating.
After the copper plating baths, the next step is to conduct tin plating on the panel. This makes it possible to remove all the copper remains left during the etching stage.
Step 6: Etching
The desired copper is protected in this stage by removing unwanted copper that will remain below the resist layer.
You can use chemical solutions to clear the excess copper. Tin will protect the valuable copper in this stage.
From here, the conducting areas and connections are now appropriately established.
Step 7: Solder Mask or Glass Glaze
For Ceramic PCB, mostly of customer will not do solder mask, it is OK. Because some of ceramic pcb the work temperature is very high, no need the solder mask.
Also, for special ceramic PCB, we can do glass glaze instead of solder mask. The glass glaze material can withstand very high temperature.
Then proceed to pass it through the solder mask ink. The portions covered will remain unhardened, ready for removal.
Pass the board through an oven. This will cure the solder mask.
Step 8: Surface Finished
To add solder-ability to your ceramic PCB, chemically plate it with either gold or silver.
For ceramic pcb, we suggest doing immersion gold, especially if you want wire bonding with gold or silver line.
Step 9: Electrical Test
This procedure will help you to confirm the functionality of the Ceramic PCB and ensuring the circuit board will not have open or short problem.
Step 10: Profiling with Leaser
This is the last step. You will cut different boards from the panel that you have made.
You have two alternative methods to achieve this. You can use a router or a v-groove. Both ways will enable you to pop out the boards from the panel easily.
Step 11: FQC
QC worker will inspect all of boards base on IPC class 2 standard or your quality standard before shipment.
Conclusion
The ceramic PCB manufacturing process includes 11 critical steps, these precise processes give ceramic PCBs excellent thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature, high-frequency, and high-power applications.

0086-755-29970700
sales@hitechpcb.com; sales@hitechcircuits.com
3F, B5 Dong, Zhimeihuizhi, FuYong, Bao’an Dist. Shenzhen, GuangDong, China 518103
 Chinese
Chinese English
English Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Portuguese
Portuguese





